Sailing: Sailing yachts exclusive novelties
People have been fascinated by sailing ships for thousands of years. They have contributed significantly to the development of human civilization. Sailing is a challenge that requires both physical and mental skills as well as a sound understanding of physics. Today, sailing has established itself as a sport and leisure activity for people of all ages. We show you exclusive innovations and trends in sailing yachts of various designs in conversation with the yacht builders.
Sailing-Classics: Sailing trips between adventure and comfort
Sailing on a large yacht, using the wind for propulsion and enjoying the comfort of a cruise at the same time - this is exactly what Sailing-Classics offers. This unique concept for sailing trips combines an authentic sailing experience with exclusive amenities and open... mehr dazuBavaria Yachts: Sailing Yacht C42 for Premium Ocean Cruising
The C42 sailing yacht from Bavaria Yachts is a sailing yacht that has no need to shy away from any competition in its price class. On Messe.TV we show you the world premiere of the yacht builder at boot Dusseldorf! mehr dazuOyster Yachts: Luxury Cruising Boats at Boot 2024
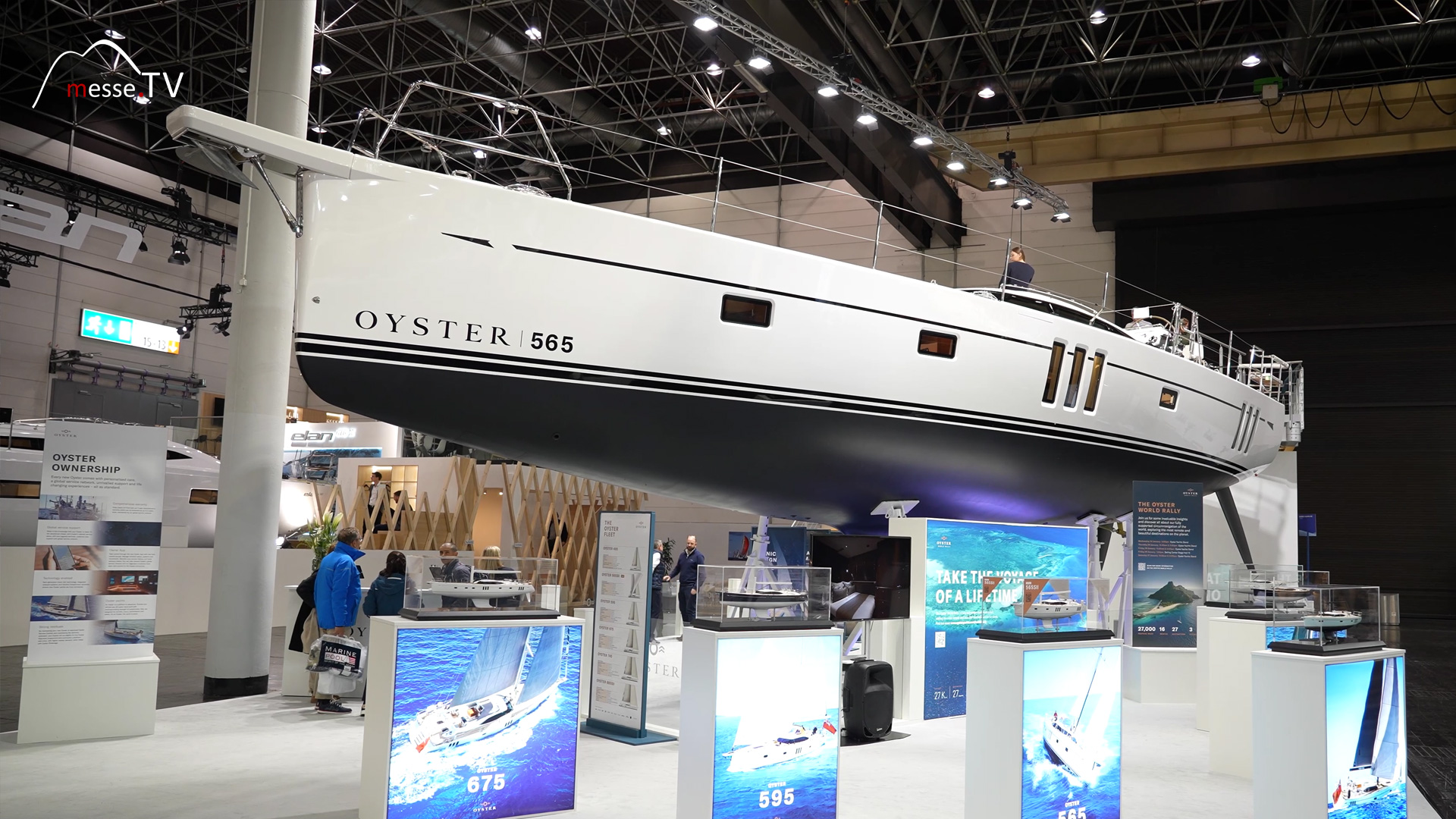
Oyster Yachts has been building boats for over 50 years. And they do so in luxurious, top-quality cruising boats. The yacht builder has brought the very popular Oyster 565 model to boot 2024. The new Oyster 565 S brings an exciting update to the market. mehr dazuJeanneau Sun Odyssey 350: Sailing Performance and Comfort Combined
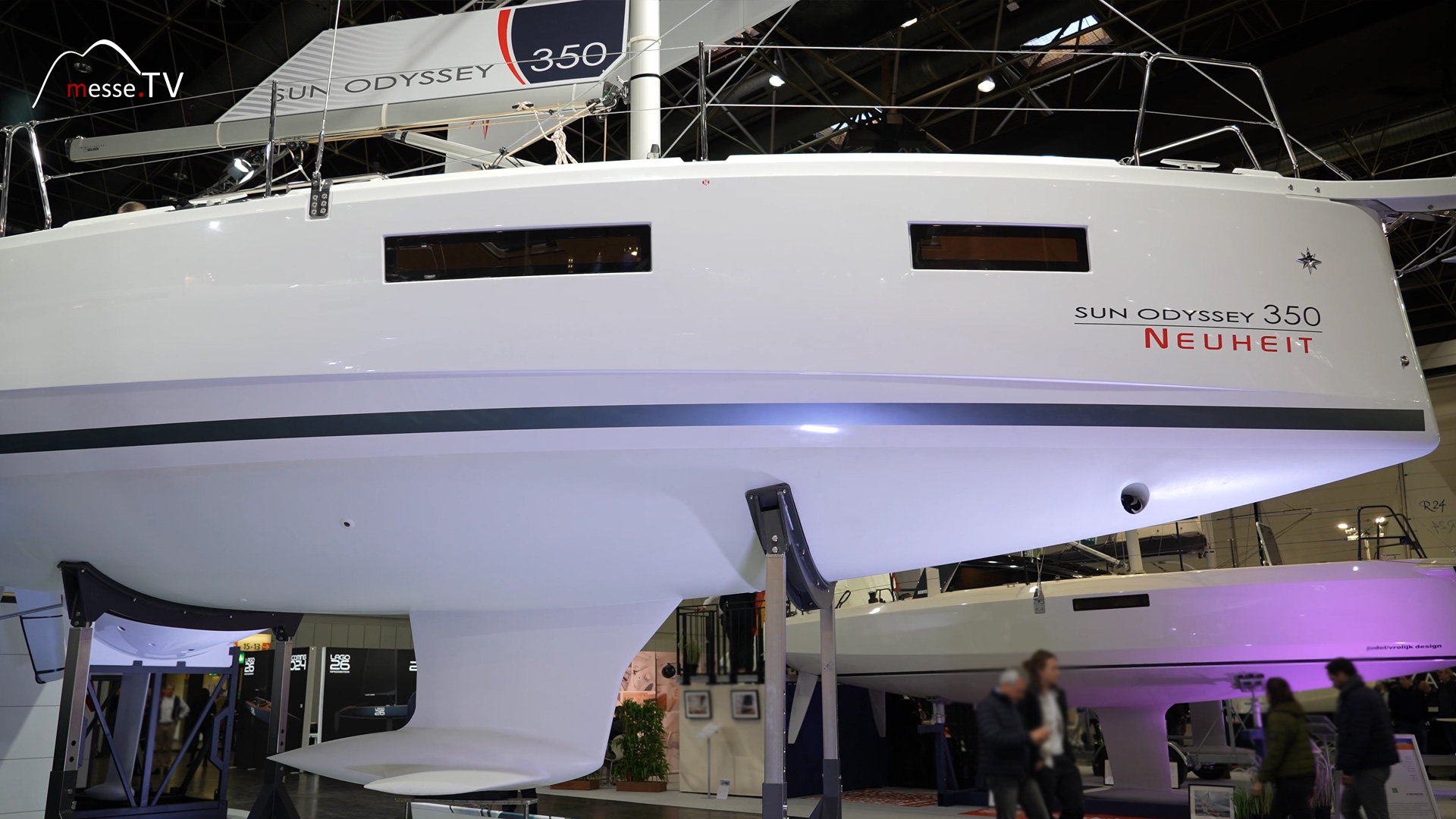
The brand new boat that Jeanneau is presenting at boot 2024 is called the Sun Odyssey 350. The boat is a real novelty. It replaces the best-selling Sun Odyssey 349, which has sold around 1500 units. Jeanneau's General Brand Manager, Samuel Dubois, is looking forward to ... mehr dazuArcona Yachts: Performance Cruisers for High-Speed Sailing
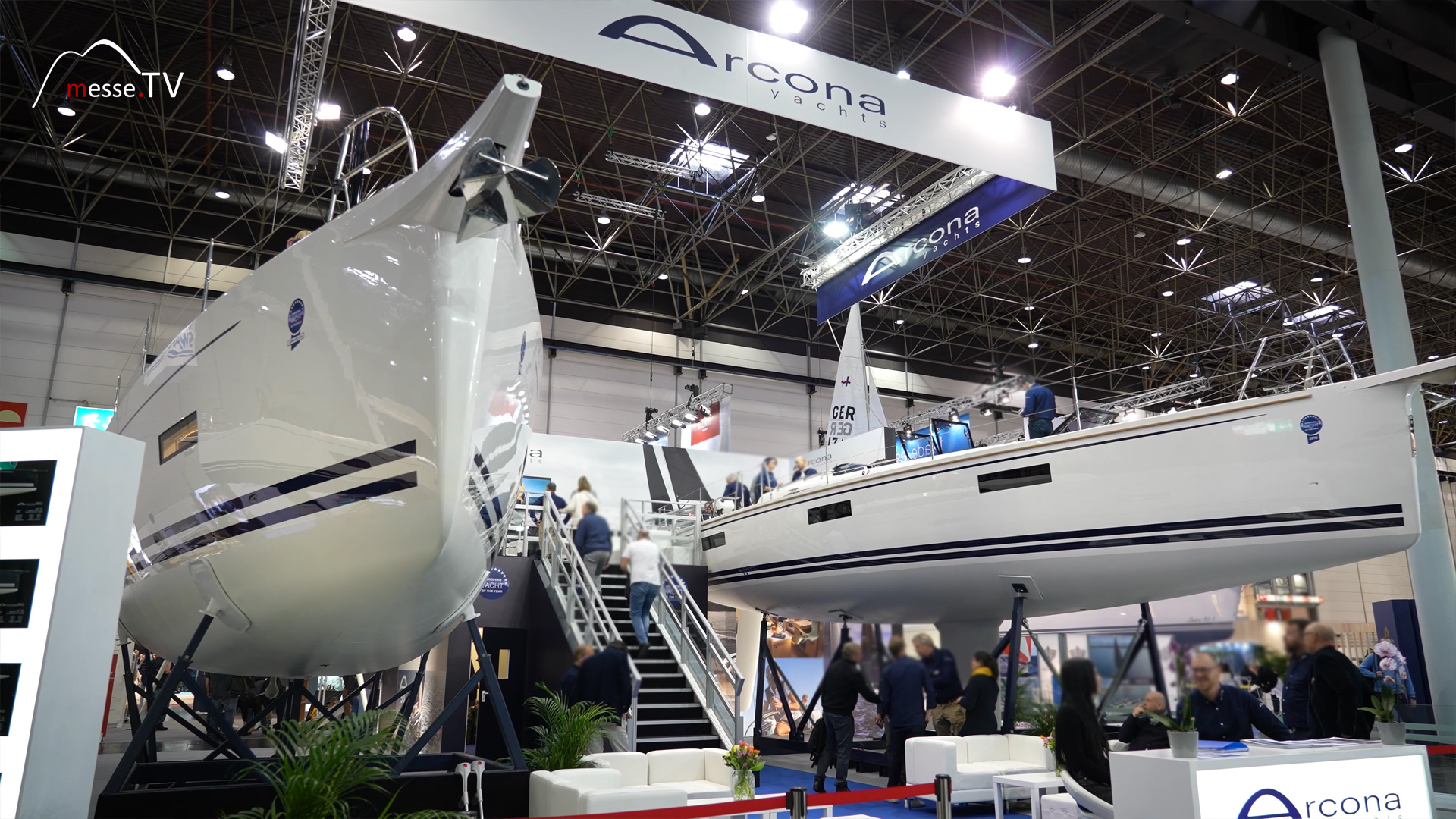
The Swedish manufacturer Arcona Yachts builds high-performance sailing boats. The company prefers to produce luxurious yachts between 34 and 50 feet in length. At boot 2024 in Düsseldorf, Arcona Yachts will be presenting its new development, the Arcona 50. mehr dazuBente Yachts: Innovative Boat and Yacht Building for Modern Sailors
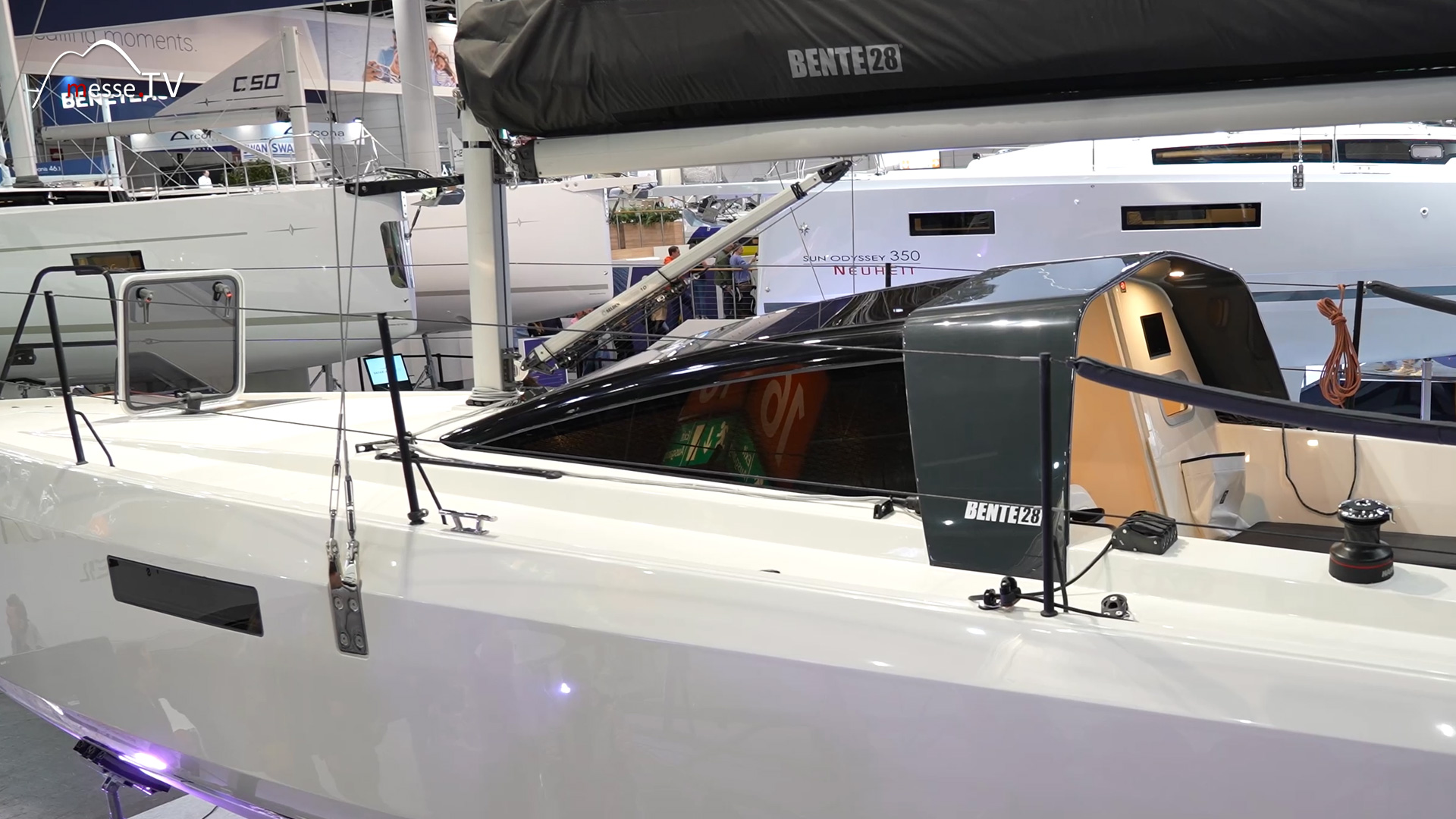
Christian, head of Bente Yachts based on Lake Constance, will be presenting the Bente 24, 28 and 39 yacht range at the boot 24 trade fair stand. All of the boat builder's boats are very performance-oriented and can be sailed very fast as well as planing. mehr dazuHallberg-Rassy: Premium Sailing Yachts for True Ocean Cruisers
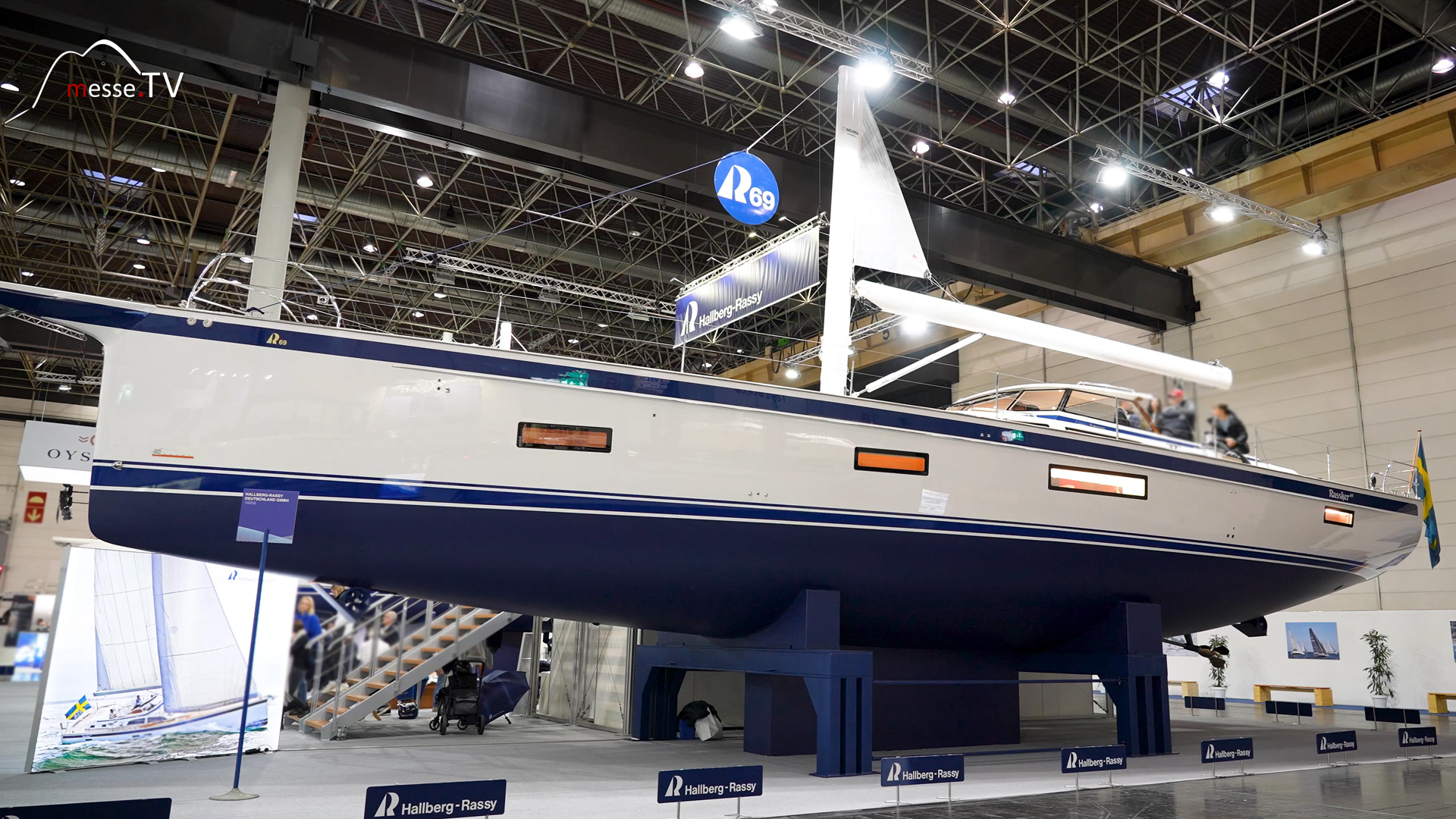
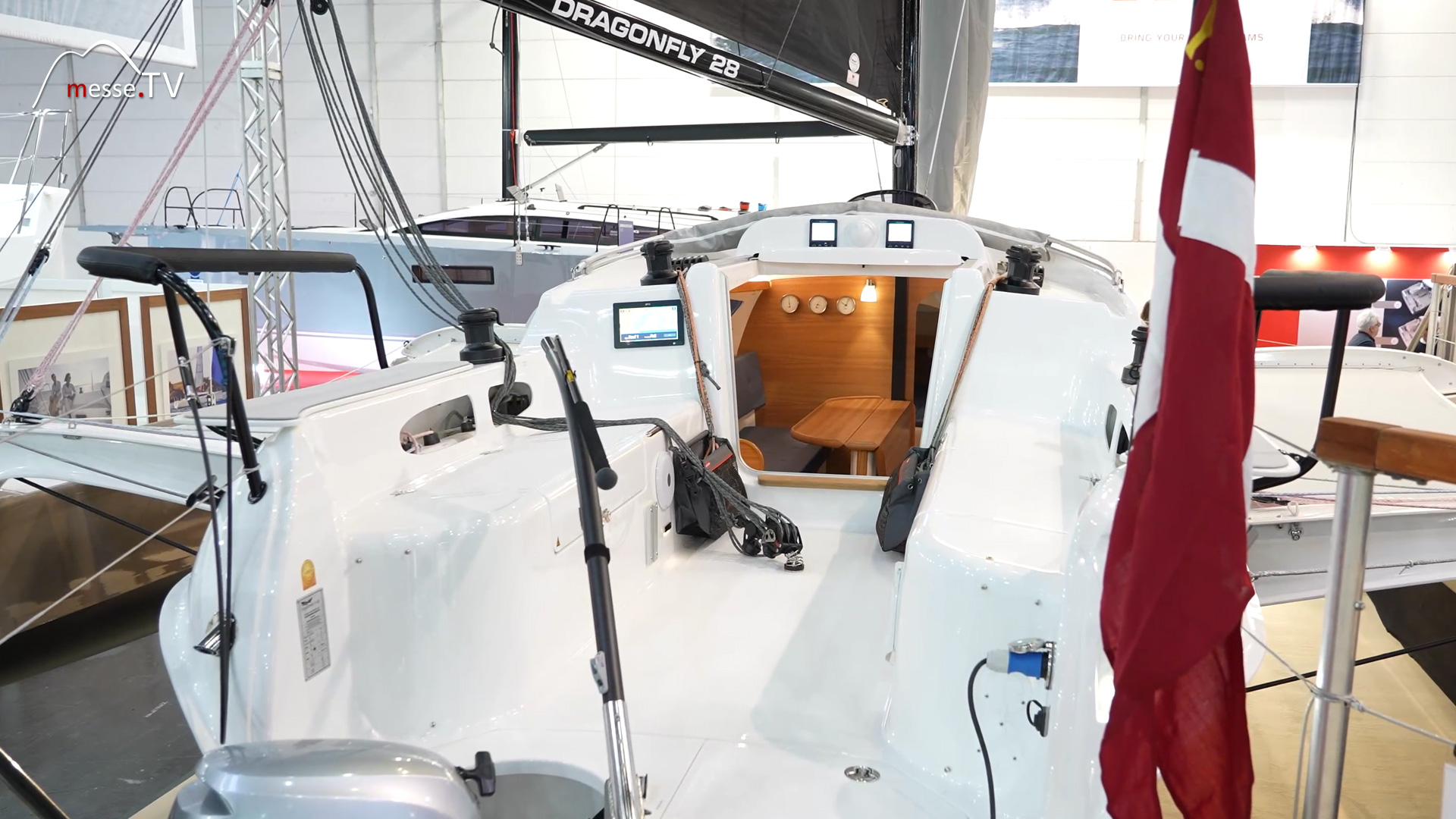
At the Hallberg Rassy stand, the Hallberg Rassy 69 welcomes us to Düsseldorf as the largest sailing boat of the entire boot 2024. It is the largest and grandest boat ever built by the company in its 80 years of existence. mehr dazuDragonfly 40 Sailboat: Cutting-Edge Design at Boot 2024
Dragonfly builds high-performance trimarans of the highest quality for cruising purposes. The trimarans can be folded, so they do not take up much space at the berth in the harbor. mehr dazuDaysailer sailboats and more - SAFFIER YACHTS
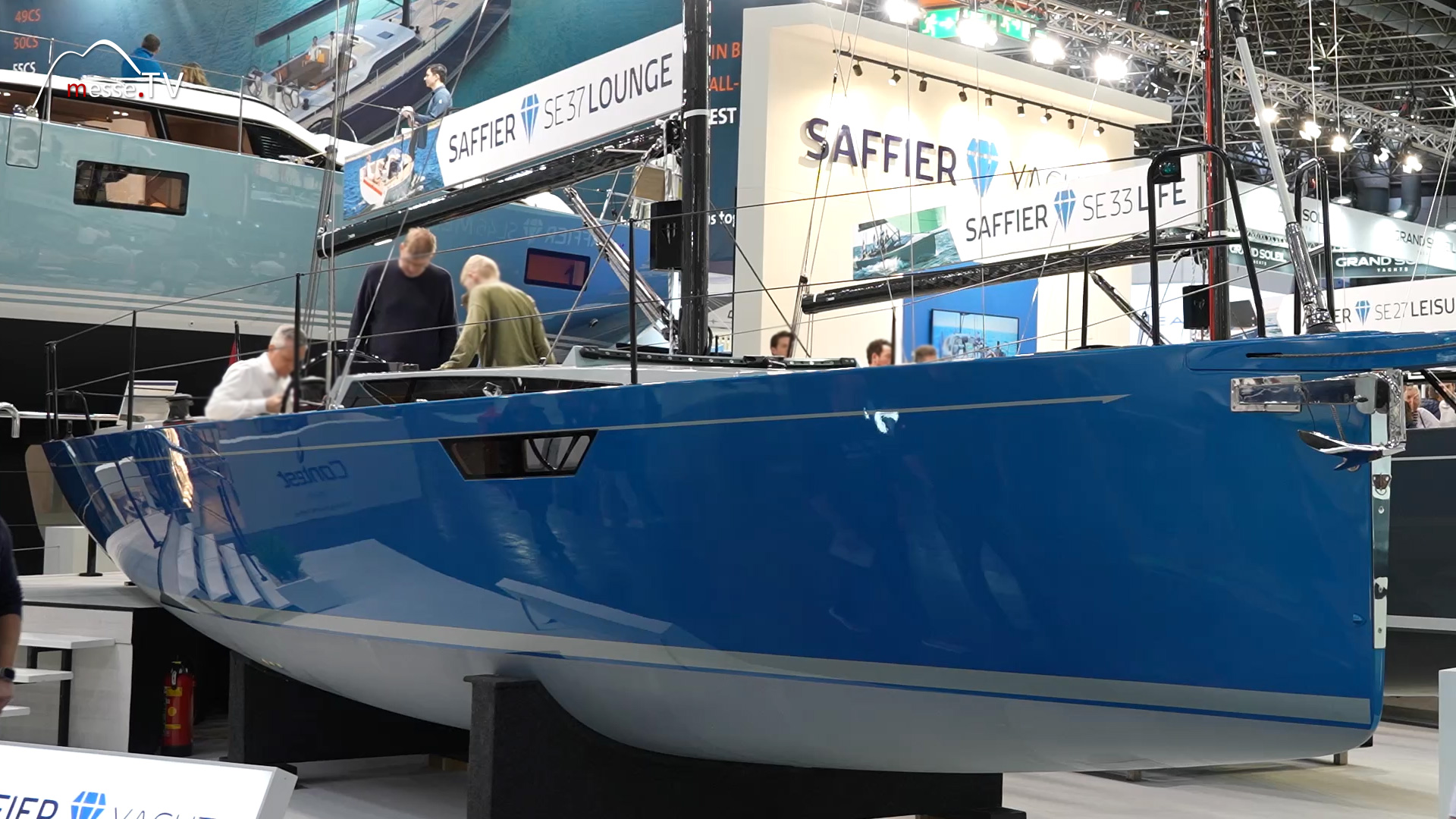
Saffier Yachts is a manufacturer of first-class small sailing yachts. The company builds 160 boats a year with a focus on small sailing yachts suitable for day and weekend cruising. The range extends from 6.5 m to 8 m and up to 37 m. The 37-meter boat can be viewed at t... mehr dazuLeonardo Yachts: Customized Daysailer for a Personal Sailing Experience
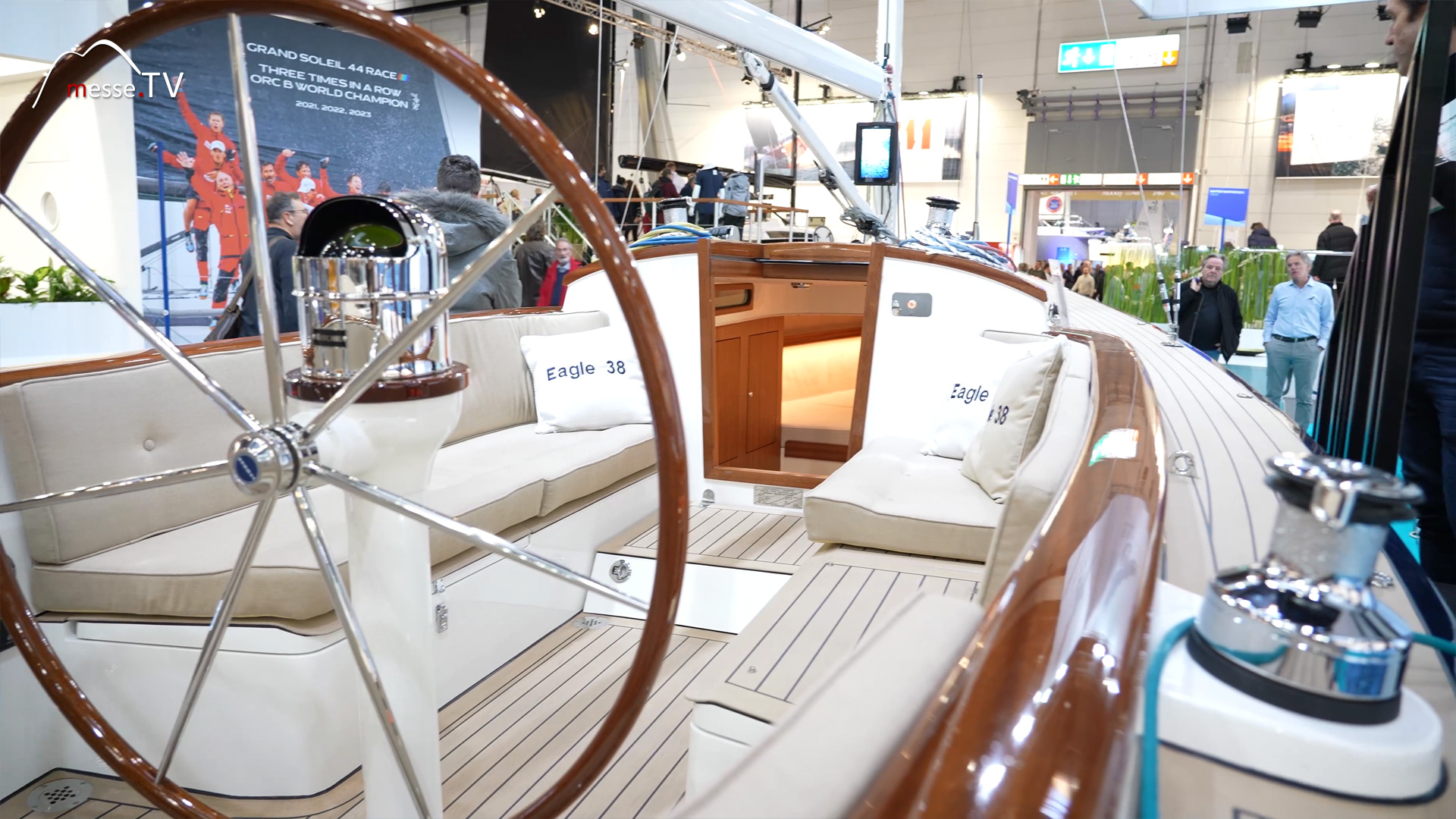
Rachel Boersma from boat builder Leonardo Yachts is presenting the Eagle 38 at boot 2024. The portfolio includes other models such as the Eagle 44, 46 and 54, and this time the Eagle 38 will be presented. Of course, the traditional classic lines stand out from modern bo... mehr dazuSunbeam Watersports: The Ultimate Weekender Sailboat for Adventure Enthusiasts
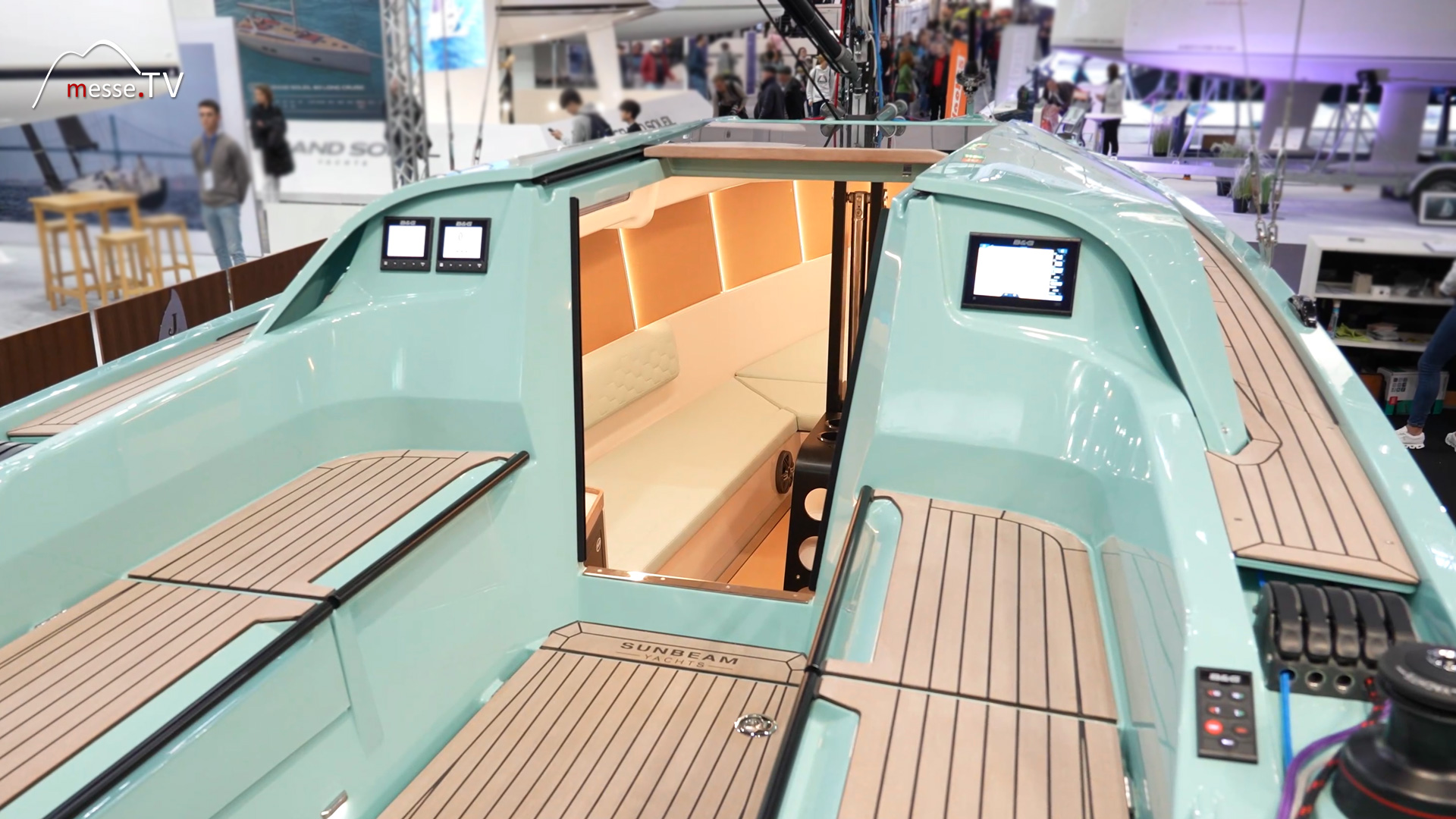
The concept of the Austrian boat builder Sunbeam is weekenders or daysailers plus. Sunbeam does not build touring boats, but neither does it build pure daysailers. The company builds boats with which you can set sail on Friday afternoon, spend a great weekend on them an... mehr dazuSailboat made of plywood and epoxy resin - RM YACHTS
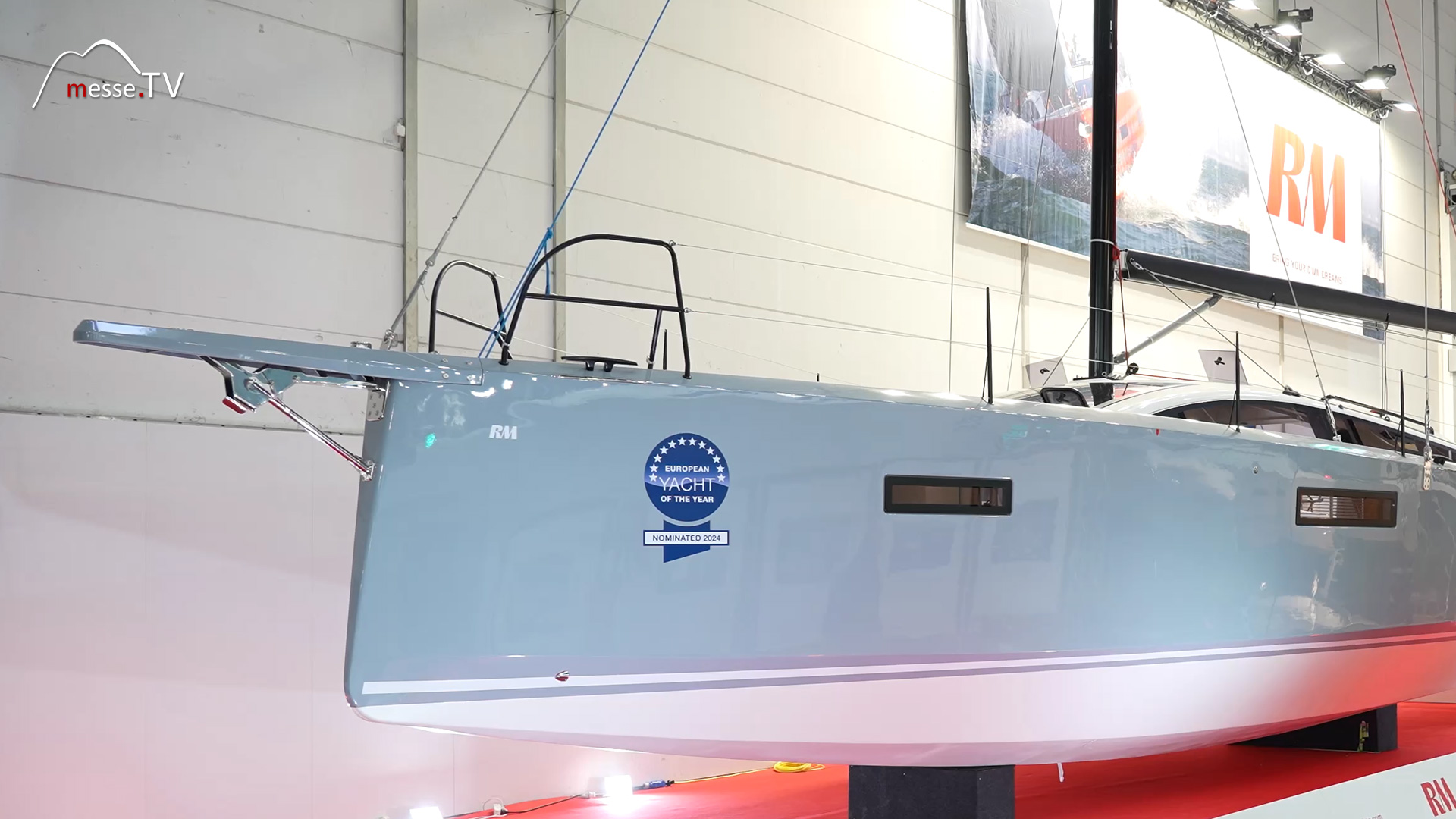
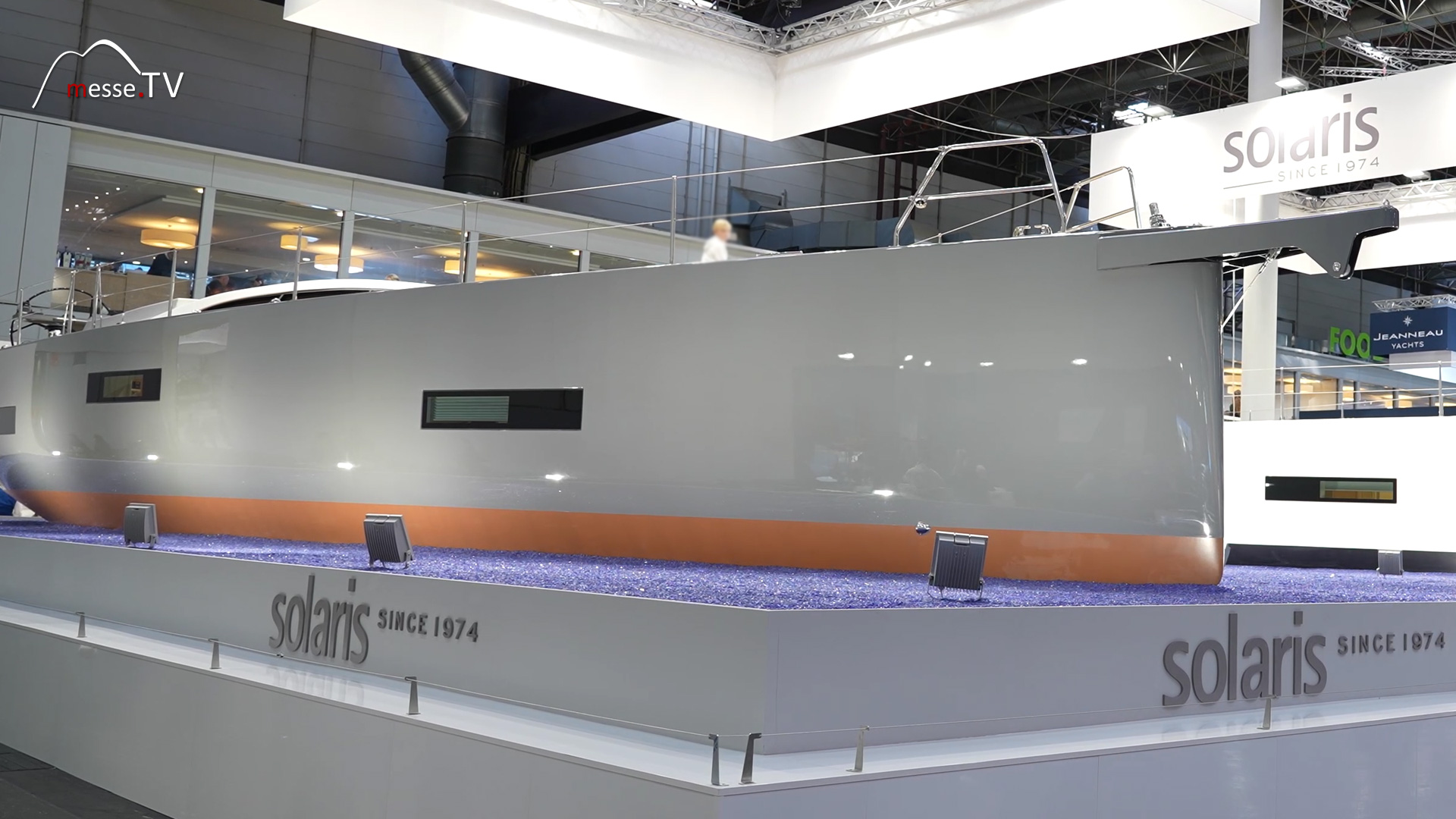
RM Yachts builds boats from plywood. This unusual construction method does not reveal from the outside that it is a wooden boat. Everything above deck is made of wood, a unique process. The company comes from France, where the small shipyard builds 30 boats a year. mehr dazuLong-term cruise yachts - SOLARIS YACHTS
Solaris Yachts sind Spezialisten für Segelyachten auf höchster Qualitätsstufe. Die Produktionswerft steht für soliden Yachtbau in der Verbindung mit High-Tech. Wir lassen uns zeigen, welche Neuheiten der Yachtbauer auf der boot 2024 vorstellt. mehr dazuBavaria Yachtbau: Luxury Yacht Series at Boot 2024
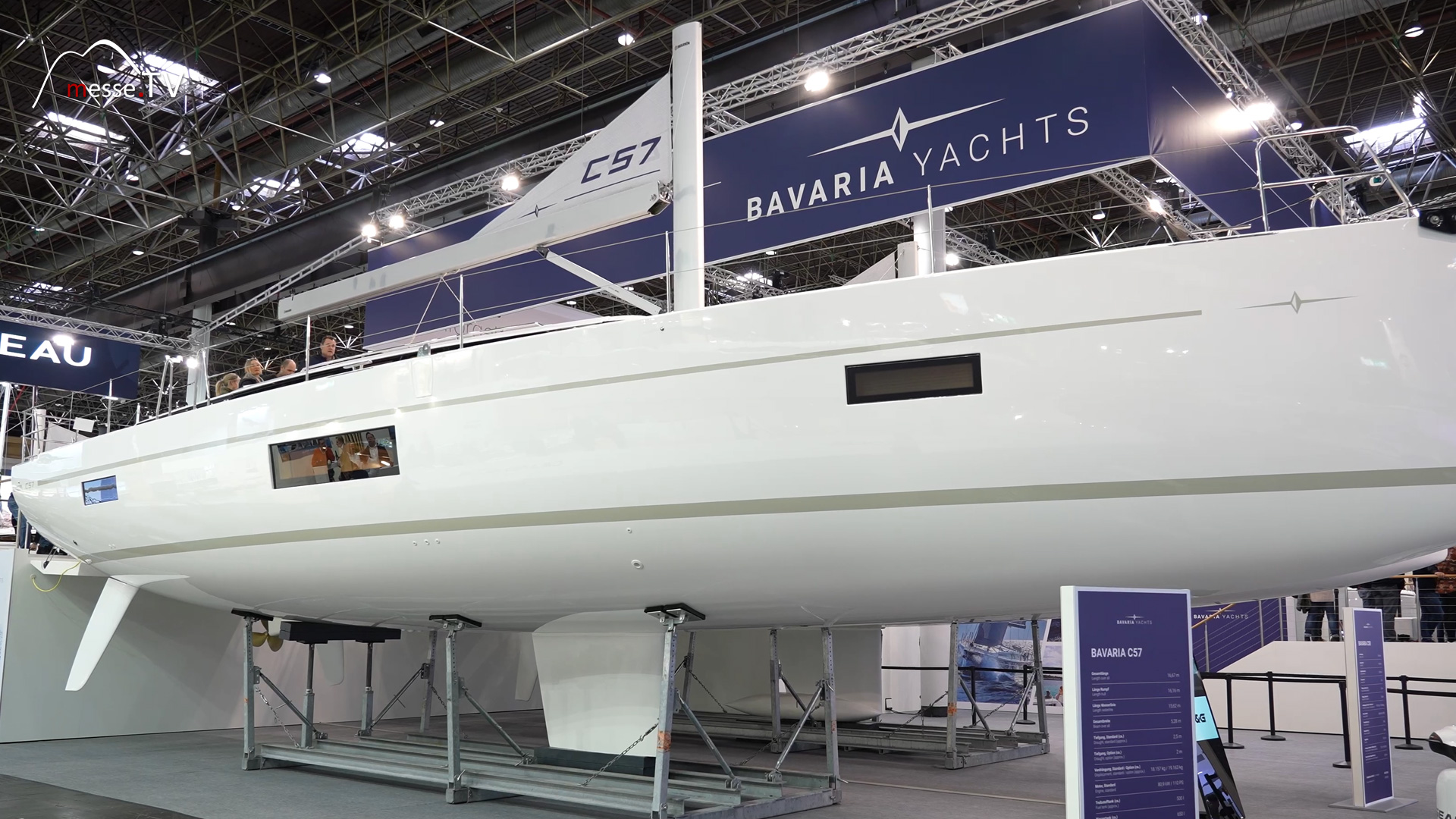
The series manufacturer Bavaria Yacht builds up to 700 beautiful yachts every year. They are wonderful to sail and offer plenty of space, they are simply beautiful. But what new products will the yacht builder be presenting at boot in Düsseldorf? mehr dazuThe most popular types of sailboats
Dinghies are small and open sailing boats with a flat bottom. The center of gravity of these boats is above the waterline. This means that dinghies can right themselves through the water pressure if they capsize. The crew can shift the boat's centre of gravity using their own body weight to stabilize the boat in strong winds and gusts. If the crew does not react in time to a change in wind pressure, a dinghy can capsize. The floats mounted on the boat and/or foam-filled cavities in the hull ensure a strong buoyancy. This ensures that the boat does not sink after capsizing. The double bottoms installed in most dinghies ensure that any water that has penetrated when capsizing drains away quickly after righting. Experts differentiate between two main categories: Racing and touring dinghies. The different types differ in terms of their intended use. Hiking dinghies are designed for leisure and hobby sailors. They are stable and offer a high level of comfort. Racing dinghies, on the other hand, are used in competitive sailing sports as they are agile and fast. Most of the larger bodies of water in Germany are home to sailing clubs that practise dinghy sailing as a sport.
Daysailers are small sailing yachts and are suitable for day trips. They are usually lightweight and equipped with a large cockpit that can accommodate the entire crew. This enclosed area offers reliable protection from the weather. Standard daysailers can accommodate three to six people. Daysailers are comfortable and user-friendly. These sailboats usually weigh 700 to 3,000 kilograms and are up to ten meters long. However, some special designs with a length of around 20 meters are still considered daysailers, as they are only suitable for day or weekend trips in terms of their other features. Experts differentiate between keelboats and centerboard boats. The former have a heavy keel, which gives the boats extra stability. The latter are equipped with a so-called centerboard. Thanks to their shallow draft, centerboard boats can navigate shallow waters. In calm conditions, an outboard motor is used for propulsion, whereas larger sailing boats use an inboard motor. The crew steers a daysailer using a so-called tiller. There are usually no steering wheels on these comparatively small vessels.
Weekenders are specially designed for extended sailing trips at weekends. Compared to daysailers, they offer additional comfort for overnight stays on board. This allows sailors to spend longer periods on the water without increasing the risk of fatigue, tension and nervous strain. Weekenders are usually equipped with a spacious cabin that can accommodate several people. Larger boats of this type have bunks, a simple kitchenette and a wet room. The designers make sure that small crews or individuals can steer a weekender. These boats are therefore suitable for amateur sailors with limited sailing experience. Weekenders are available in various sizes, from small keelboats to cabin cruisers. This type of boat is the ideal choice for all sailing enthusiasts who are looking for an easy-to-steer and inexpensive sailing boat and at the same time want to go on longer trips.
Sailing yachts Sailing yachts are larger leisure and sports vessels that use their sails as their primary means of propulsion. Sailing cruisers and regatta yachts in particular belong to this type of vessel. Colloquially, the term also covers dinghies, daysailers and weekenders. Sailing yachts are suitable for longer trips with many overnight stays at sea. They offer sailors a spacious and comfortable cabin with sleeping berths, a kitchen and a bathroom. Sailing yachts are usually equipped with a solid keel, which ensures the stability of the ship even in heavy seas. This type of vessel also includes regatta yachts designed for competitive sailing. These boats are streamlined and built from particularly lightweight materials, making them extremely fast and maneuverable. The speed record for this type of boat is currently 65.45 knots. This corresponds to around 121 kilometers per hour and thus the speed of motor vehicles on freeways. Swiss engineers are working on a regatta yacht that should significantly exceed this speed record. If chief engineer Mayeul van den Broek achieves his ambitious goals, the sailing yacht will reach a top speed of 80 knots (148.16 kilometers per hour) under the name "SP80".
Multihulls are sailing boats that consist of several hulls. Catamarans and trimarans are among the best-known representatives of this type of vessel. Multihulls usually offer more interior and exterior space than monohulls. As the hulls stabilize each other, these ships can withstand heavy seas. Catamarans are the best-known multihulls. They consist of two parallel hulls, usually of the same size and with a similar cross-section. Catamarans are suitable for long voyages and transporting heavy loads. Trimarans consist of three hulls arranged in a line. The middle hull, in which the cabin is located, is longer than the two outer hulls. Due to their design, trimarans are fast, stable and maneuverable. They are mainly used in sporting competitions.
What is single-handed sailing? Single-handed sailing is the sailing of a larger boat with only one person on board. "Hand" is the English term for a crew member. The term "single-handed sailing" therefore describes the crew strength and not, as is often assumed, the operation of the boat with just one hand on the body. A voyage lasting several days, weeks or months places a physical and psychological strain on the sailor. In addition to loneliness, lack of sleep is a danger, as tiredness reduces concentration and performance and impairs the perception of sources of danger. The risk of developing psychiatric symptoms also increases, including listlessness, depressive moods, increased irritability and hallucinations. To reduce physical exertion, the boats are usually designed so that the sailor can perform all maneuvers from one place. All halyards and sheets are located in the cockpit so that the single-handed sailor does not have to move far away from the helm when hoisting, reefing or recovering the sails. Modern boats are equipped with self-steering systems that allow the sailor to rest and sleep, thus reducing the risk of sleep deprivation and psychological complaints.